
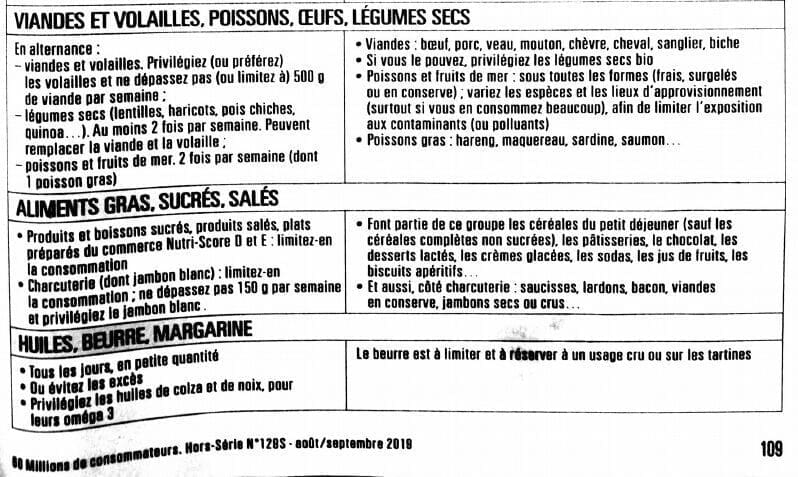
Overview of major recommendations (2019), along with advice and details to help follow them better:
| Main Guideline | Additional Information |
| FRUITS AND VEGETABLES | |
| At least 5 portions per day (each 80–100 g). | In all forms: fresh, frozen or canned – try to increase your intake.1 No more than one glass of fruit juice per day (preferably made from whole fruit). Dried fruits should be consumed occasionally, as they are high in sugar. If possible, choose organic fruits and vegetables. Nuts2 (unsalted) (almonds, hazelnuts, walnuts, pistachios… etc.): → 1 small handful per day |
| BREAD, PASTA, RICE, SEMOLINA, POTATOES | |
| 1 portion at each meal At least one wholegrain or semi-wholegrain product per day | If possible, choose organic cereal products. Among breakfast cereals, only unsweetened wholegrain cereals belong to this group. |
| MILK, YOGURT, CHEESE | |
| 2 portions per day | → 1 portion = 150 ml of milk = 125 g of yoghurt = 30 g of cheese Remember to take into account the milk and cheese already included in the dishes you prepare. Due to the risks linked to contaminants (or pollutants), make sure to vary dairy products. |
| MEAT AND POULTRY, FISH, EGGS, LEGUMES | |
| Alternate between meat and poultry: Favour poultry and do not exceed (if possible) 500 g of meat per week. Legumes (lentils, beans, chickpeas, quinoa, etc.): At least twice a week; they can replace meat and poultry. Fish and seafood: twice a week, (including one oily fish.) | Meats include: beef, pork, veal, lamb, goat, horse, wild boar, venison. If possible, choose organic dried legumes. Fish and seafood can be consumed fresh, frozen or canned; vary species and sources (especially if consumed frequently) to limit exposure to contaminants (or pollutants). Oily fish: herring, mackerel, sardines, salmon… |
| FATTY, SWEET, SALTY FOODS | |
| Sweet foods and drinks, salty foods, and commercially prepared meals with Nutri-Score D or E: Limit consumption. Processed meats (including cooked ham): limit consumption; do not exceed 150 g per week, and favour cooked ham. | This group includes breakfast cereals (except unsweetened wholegrain cereals), pastries, chocolate, dairy desserts, ice cream, sweets, fizzy drinks, fruit juices, savoury snacks, etc. Also included among processed meats: sausages, bacon, lardons, canned meats, dry-cured or raw hams. |
| OILS, BUTTER, MARGARINE | |
| Daily, in small quantities or avoid excess. Prefer rapeseed (canola) and walnut oils for their omega-3 content. | Butter should be limited and reserved for raw use or on bread. |
(French Original Version):

Cancer Research UK (Healthy Balanced Meals):
Please find in this schema what it is advise to eat for each meal to keep Healthy Balanced Meals :

Preparing 3 Food Product Categories for Each Meals:
- 50% of Veggies ( Mixing Veggies is good idea and also using Good Quantity of Green Veggies: Spinach, Broccoli, Haricot, etc )
- 25% of Protein ( Reminder : Vegetarian Protein are less absorbed than Animal Protein just to keep in mind in case you increase your activities )
- 25% of Grains and Carbs can be alternate to every meal ( Wheat, Rice, Potato, Pulse, Quinoa, Buckweat …) More informations on this (Link)
Do not forgot “Grains” in your plate. (Culturally it might sound “Different” or “Uncommon”) But if you do it you will feel globally better, Grain are providing lot of different “Vitamin” but also help Transit, “Liver Function”, Absorption and Weight.
As an example “Pulse” contain a lot of Vitamin B, if you try to eat Pulse Twice a Week, there is lot of chance you notice good positive effect rapidly.
Try to Eat a Wide Range of Vitamins:
The graph bellow is an “Example” of Vitamin Type associate to Food Products. Remembering it is better to Eat with Diversity than Quantity. Understanding also Food products, do not contain all the same Type of Vitamins. For more informations regarding Nutritious Topic please find the (Link) and also Books from Jean-Marie Bourre (Link)
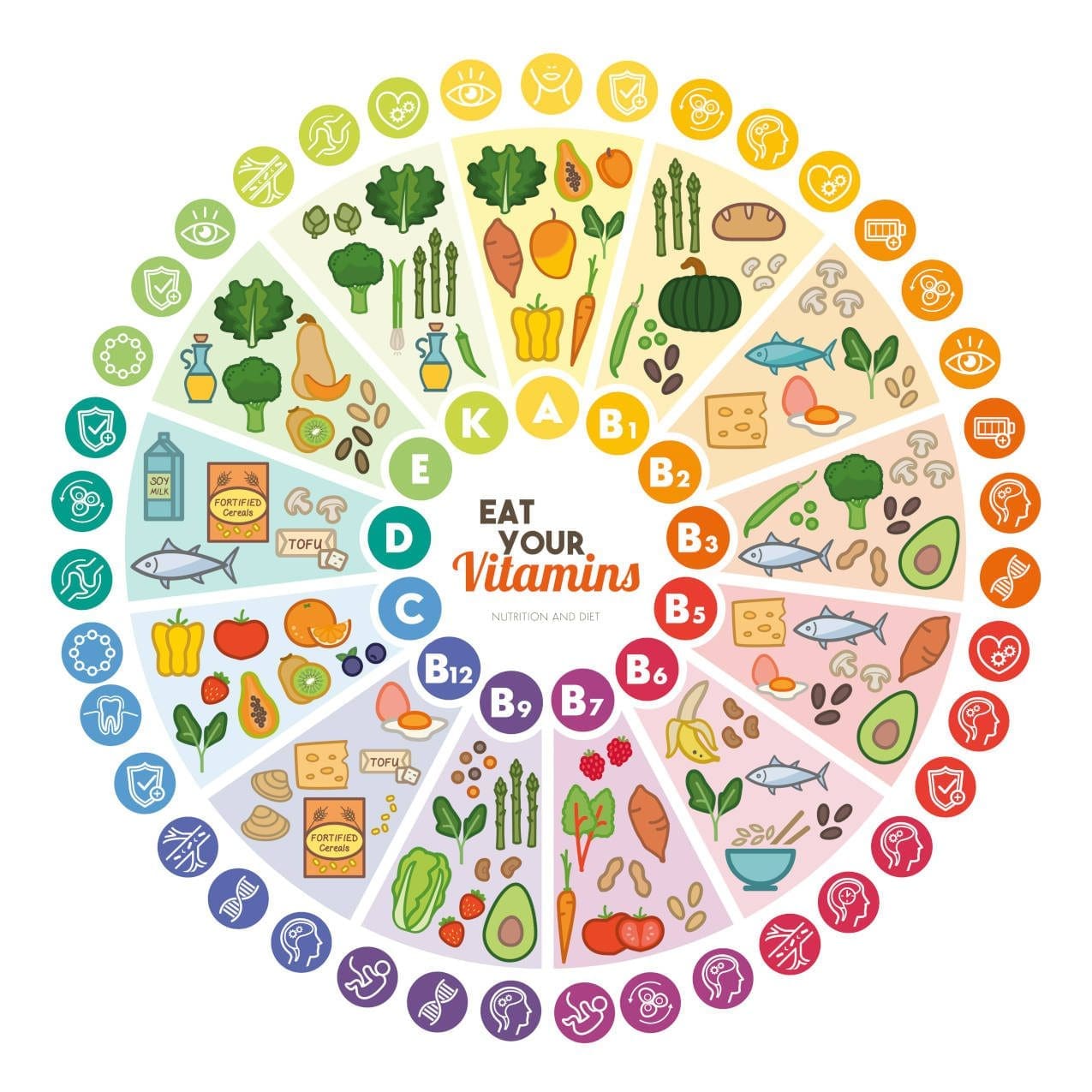
Always remember, natural food products are better than vitamin supplements. (Link) Also, remember that tea increases the risk of anaemia.
Comments are closed